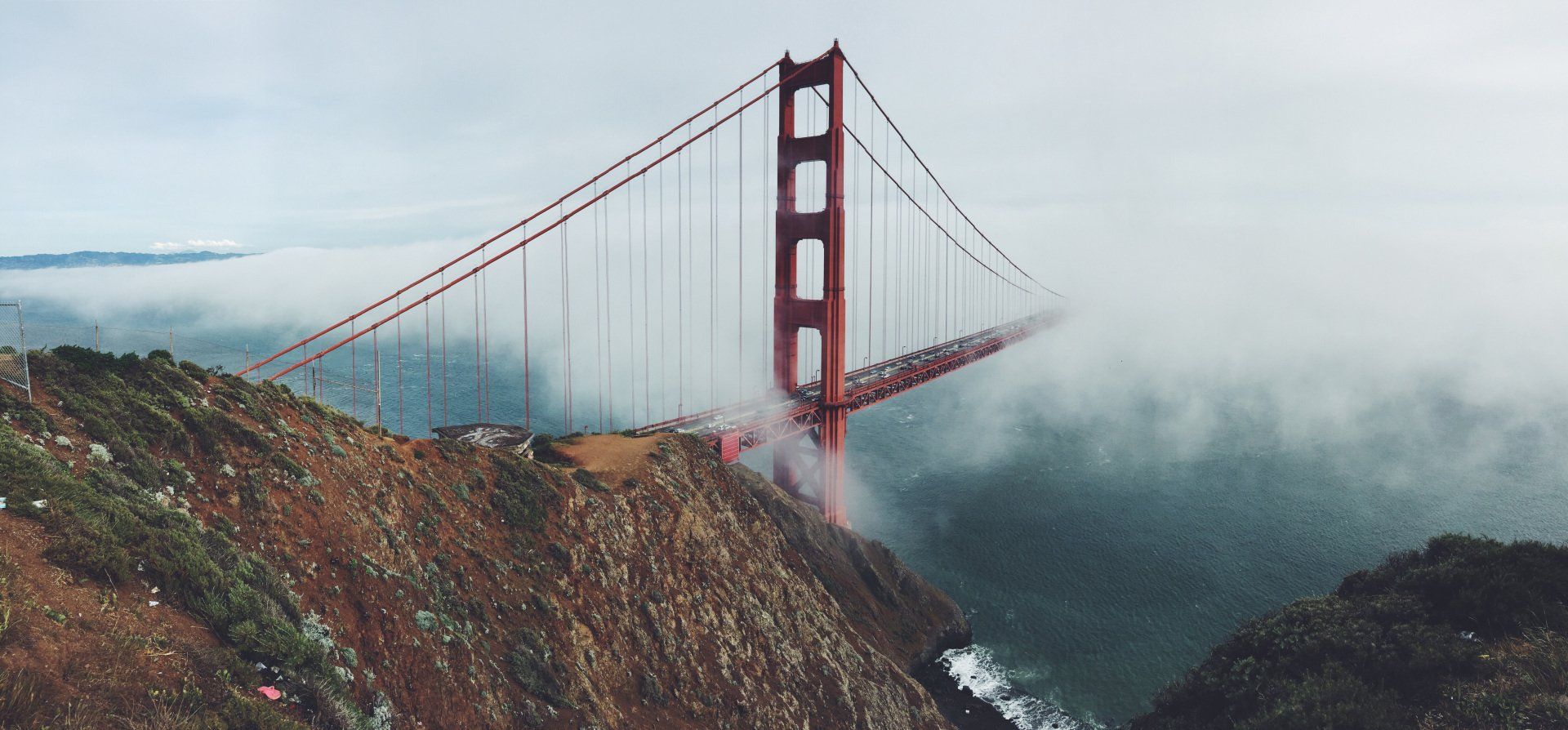
Why Is There No Light In Space?
Why Is There No Light In Space?
As we gaze out into the vast expanse of space, we can't help but feel awe-inspired and intrigued by the enigmas of the cosmos. However, despite the immense amount of matter present, why does the darkness and emptiness seem to prevail? Keep reading to unravel the reason behind the absence of light in space.
The science behind light
What is light?
Light in its basic form is a type of wave not all that different from the ones seen in the ocean. However, light is radiant energy that has to originate from an object. Humans need light to be able to see, and its absence results in complete darkness.
We can see only a tiny part of the much larger electromagnetic spectrum, conveniently called visible light. This portion of the spectrum includes the colors of the rainbow, from red to violet.
Where does light come from?
As previously stated, light always has a source. In the domain of astronomy, stars are capable of generating light particles by releasing energy from their core. Through the fusion of two hydrogen atoms into a single helium atom, the reaction generates both heat and light.
Subsequently, these light waves propagate away from the star at a constant speed of 299,792,458 meters per second (983,571,056 feet per second) through the vast expanse of space. For instance, at a distance of approximately 93 million miles (150 million kilometers), it takes just 8 minutes and 20 seconds for light waves to travel from the Sun to the Earth.
What objects in space can create light?
Despite the abundance of objects scattered across the universe, not all of them have the capability to produce light. The reason being that the conditions required for nuclear fusion, namely extreme pressure and temperatures surpassing 10,000,000 Kelvin, cannot be met by most cosmic entities.
Even though some celestial bodies such as rocks found in the Solar System or beyond may have a molten core, their temperatures will never reach those of a star. Hence, rocky planets and moons lack the ability to emit their own light and must rely on light from nearby stars to be visible.
It is noteworthy that the larger planets in our Solar System, such as Jupiter and Saturn, do radiate a faint amount of light by themselves. Though relatively insignificant in comparison to a star's brightness, these planets are massive enough to generate light waves through the force of their gravitational pulls.
Why does Earth's Sky look blue during daytime?
In order to grasp the reason for the absence of light in space, it is helpful to first comprehend why daylight occurs on Earth.
Unlike the vacuum of space, Earth has an atmosphere composed of various types of gas molecules. Due to the Sun's proximity to Earth, we receive a substantial amount of light from its surface.
When these light waves collide with the molecules in our atmosphere, blue and violet wavelengths are the right length to scatter. As a result, we perceive a blue sky and the side of the Earth facing the Sun is illuminated.
However, as the Sun sets, the light waves no longer reach the side of the Earth that is no longer facing it. Since light travels in a straight line until it encounters an object, these same waves are unable to reach far enough into the Earth's shadow to produce light. This results in the familiar darkness of space.
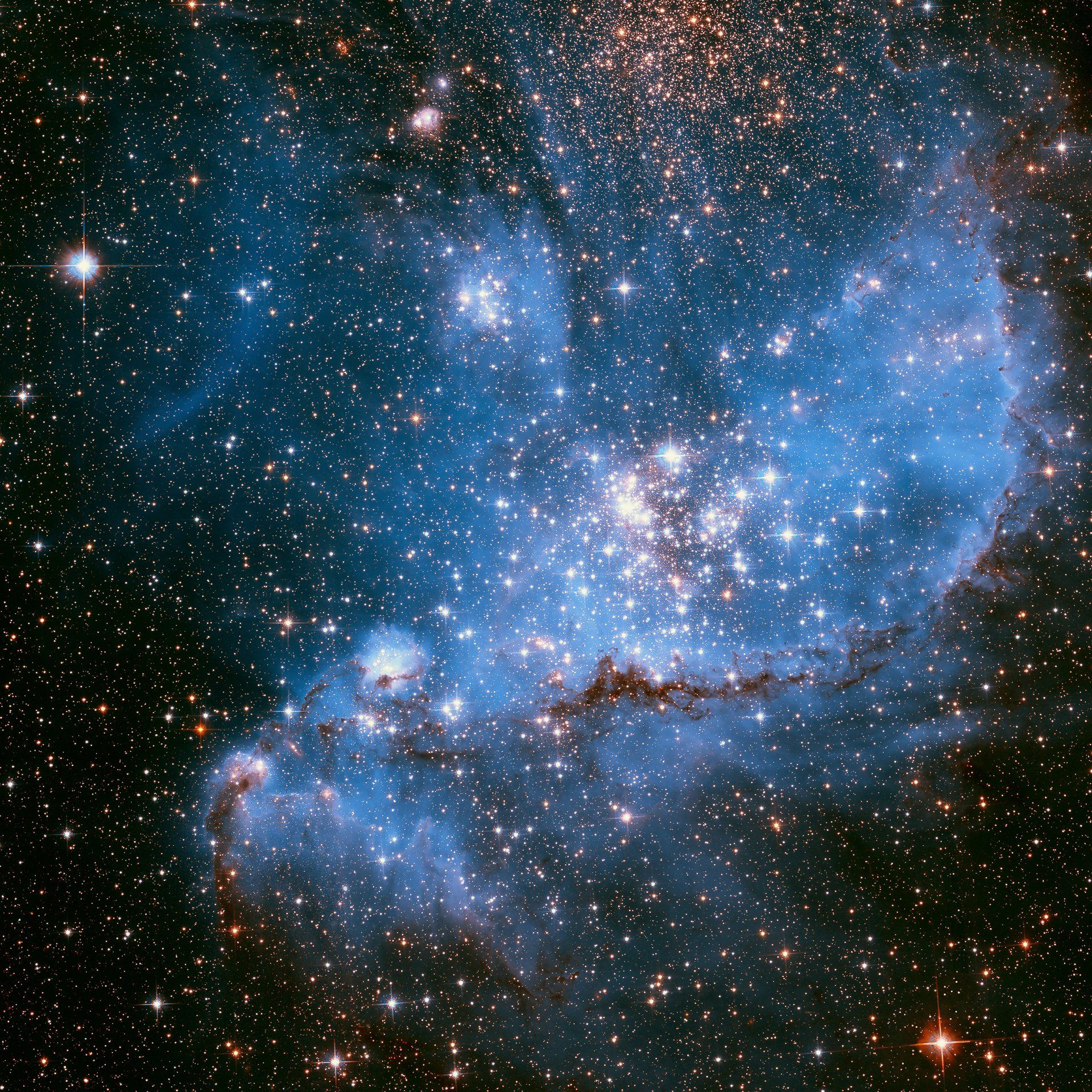
So why is space so black?
After the Sun sets, thousands of stars become visible in the night sky. However, these stars don't produce the same effect as our Sun. The reason for this is distance. The nearest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, is located 4.25 light-years away, which means it takes light about four and a quarter years to travel from the star to Earth at a speed of 983,571,056 feet (299,792,458 meters) per second.
When a star like Proxima Centauri emits light, it doesn't just travel in the direction of Earth. The light spreads out in all directions, and only a tiny fraction of that light ultimately reaches Earth. As a result, stars appear as mere points of light.
Although there is a lot of light in space due to every star shining bright, we can only see the light that enters our eyes directly. Light that travels in other directions remains invisible to us, as there is nothing in space for it to bounce off of.
New findings - space isn't so black
NASA's New Horizons spacecraft was designed to explore Pluto and uncover its mysteries, and now it has reached the outer edges of the Solar System. In this remote region of space, the darkness is ten times deeper than anything that the Hubble telescope can see.
With no interference from Earth's light pollution, New Horizons has become a powerful tool for measuring the cosmos. By activating its sensors, scientists can detect the faint glimmers of light emanating from the countless stars and galaxies beyond our own.
Interestingly, more than half of this light remains unexplained by the number of known galaxies in the scanned direction. Is it possible that there are undiscovered luminous objects beyond our detection range, or is some other phenomenon at play? Only time will reveal the answer.
Why is the moon sky black?
The Moon lacks an atmosphere, which distinguishes it from Earth. Consequently, the Sun's light can reach the Moon without any interference from gaseous molecules, resulting in the full spectrum of visible light hitting the lunar surface.
© Copyright 2021 Space-facts.co.uk
View our other facts sites: www.animal-facts.co.uk